Introduction
The Q3 GDP report showed the US economy grew at a 4.9% annualized rate, exceeding analyst estimates. However, markets seemed unimpressed as the report contained some warning signs about the outlook. While consumer spending and business investment drove the GDP growth, disposable income fell 1% during the quarter.
US Census Bureau
This indicates consumers are dipping into savings to maintain spending. Indeed, the personal consumption expenditure report showed the personal savings rate dropped to just 3.4%, a new low. Additionally, the University of Michigan consumer sentiment survey fell in October, signaling some reticence among consumers.
U of Michigan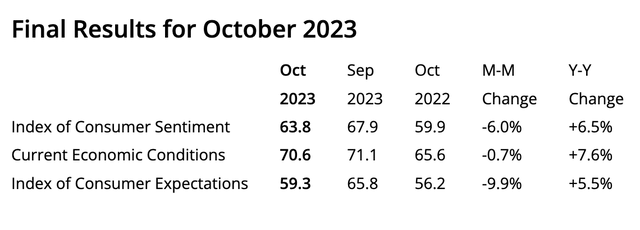
These data points suggest a mixed picture for consumer spending in the fourth quarter and into 2024. Many CEOs have expressed caution and are maintaining lean inventories. For example, the CEO of Skechers (SKX) said they remained cautious for Q4 and 2024 as they have shrunk inventory 24% below 2022 levels. This leaves the consumer sector an area to watch cautiously in the near term.
Beyond consumer spending, some sectors fueled by strong investment look more promising, such as semiconductors boosted by the CHIPS Act and artificial intelligence. The GDP report showed solid business investment, indicating companies are still spending on technology and expansion despite economic uncertainties. Areas like semiconductors and AI, which see ongoing corporate and government investment, may offer brighter spots for investors to focus on.
Intel’s Q3 Earnings Beat
Intel (NASDAQ:INTC) reported its Q3 2023 results, showing that its financial performance was improving sequentially from Q2 and had returned to EPS growth in Q3.
INTC
Further, Intel expected that both revenues and earnings per share would return to growth in Q4, with revenue growth of 8% and EPS up 193% on a year-over-year basis. The Q3 results and Q4 guidance from Intel are actually great news, thus its stock price jumped 10% following the earnings release.
INTC
Optimism Surrounding Intel’s IDM 2.0 Strategy
As our previous article suggested, we are optimistic about Intel and its IDM 2.0 strategy because through both opening its foundry service to external customers and collaborating with TSMC (TSM) on utilizing its advanced manufacturing capability, Intel can first maximize the use of its mature node technology and lower its manufacturing costs. Second, Intel’s advanced chipsets will no longer be constrained by its own foundry manufacturing development process. This will improve profitability and revenues in both the foundry and chipset segments of Intel’s business.
Further, advanced packaging technology is redefining what is possible with mature node technology, which means that there will be more cost savings opportunities from leveraging the combination of mature and cutting-edge manufacturing techniques in chip customization design. Thus, we see that owning the foundry business can provide flexibility and cost advantages in chip customization. In addition, along with increasing geopolitical conflicts, owning an integrated supply chain and securing manufacturing capacity in advance will gain an advantage in providing supply certainty, especially for large tech customers who often need to launch products in a timely and large-scale manner.
Intel’s foundry revenues actually saw sequential growth of 34% in Q3 over Q2 or 298% year over year, which currently supports the momentum behind this IDM 2.0 strategy.
INTC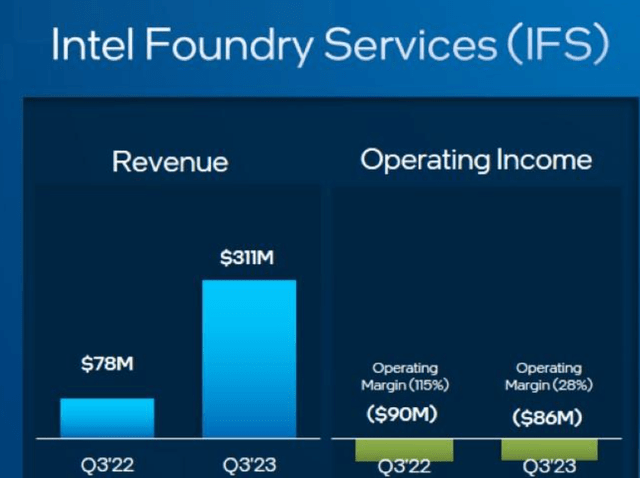
Intel’s Strategic Focus on B2B AI Market
Intel’s strategic focus on supplying AI chips for the B2B market positions the company to benefit from the strong growth anticipated in this sector.
Current AI development and adoption trends favor B2B applications over consumer ones, as AI’s utility is more productive presently in enterprise settings. Despite economic headwinds like inflation that cause uncertainty in 2024’s consumer tech market, the B2B sphere, especially AI, should see robust growth. Major tech firms including Microsoft (MSFT), Amazon (AMZN), Google (GOOG) (GOOGL) and Meta (META) have indicated as much, announcing plans to invest more in AI over the next couple of years. Thus, this space offers investors confident visibility.
Intel is poised to capitalize on this AI trend through partnerships and products. Microsoft’s announcement that Windows 11 will support Intel processors allows Intel to swiftly expand its B2B user base amid the projected AI boom. This partnership also broadens Intel’s reach faster than competitors focused on the cloud. Moreover, Intel is aggressively expanding into this space with its launch of AI PCs. The concept of AI PCs for enterprise users not only maximizes Intel’s serviceable market to help scale but also eases customers’ data security concerns since processing occurs on-device.
Valuation
Analysts predict that Intel’s forward PE ratio for 2024 and 2025 will be 17.3x and 12.3x, respectively, with robust growth of 110% and 40% expected over the next two years. We see its valuation is still appealing.
Seeking Alpha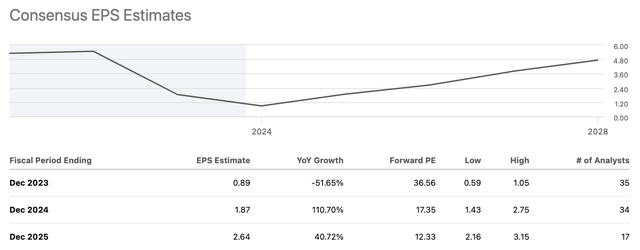
Taking into account that Intel has surprised analysts for three quarters running and that its five-node strategy is on schedule. Its projected future sales and EPS growth are supported by the existing development’s pace and progress. Thus, it appears that there is a moderate probability of missing estimations.
Seeking Alpha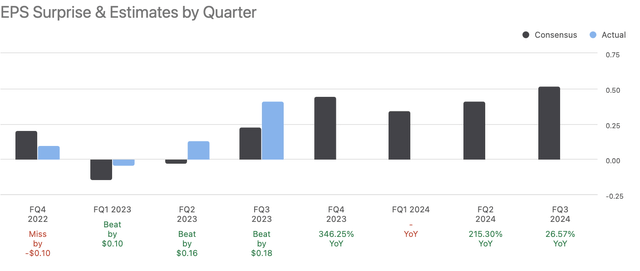
Risk
Intel continues to face competitive risks as Nvidia gains a share in the data center market. Intel’s current strategy centers on increasing AI usage beyond the cloud, similar to AMD (AMD), and providing custom solutions to differentiate itself. Additionally, Nvidia recently announced plans to develop Arm-based PC chips, potentially increasing competitive pressure on Intel. While Arm chips currently focus on energy efficiency rather than performance, limiting near-term risk, investors should monitor this development.
Intel’s IDM model has drawn some investor criticism regarding potential conflicts of interest with customers interested in designing their own chips. If key customers currently using Intel’s chips pursue their own manufacturing, it could negatively impact Intel’s long-term outlook. However, we believe Intel’s advances in process technology like Intel 3 and Intel 18A, along with advanced packaging partnerships with TSMC, help mitigate this risk by maintaining Intel’s manufacturing leadership.
Conclusion
Investors seeking stability and growth should take a closer look at Intel, as we see it as one of the more certain growth fields in 2024 compared to the uncertainty facing the consumer sector. We believe Intel’s turnaround story is compelling, backed by evidence that its IDM 2.0 strategy is gaining traction, along with its focus on the B2B AI market and the advantage of owning an integrated supply chain to secure manufacturing capacity for customers.
Even though there is fierce competition risk in the market, we see that Intel appears well-positioned to deliver improving execution and strong growth over the next few years based on its manufacturing and strategic initiatives. For investors looking to add exposure to secular growth trends like AI computing while limiting macroeconomic risk, Intel stands out as an attractive opportunity relative to consumer-driven sectors facing unpredictable demand.
Read the full article here







